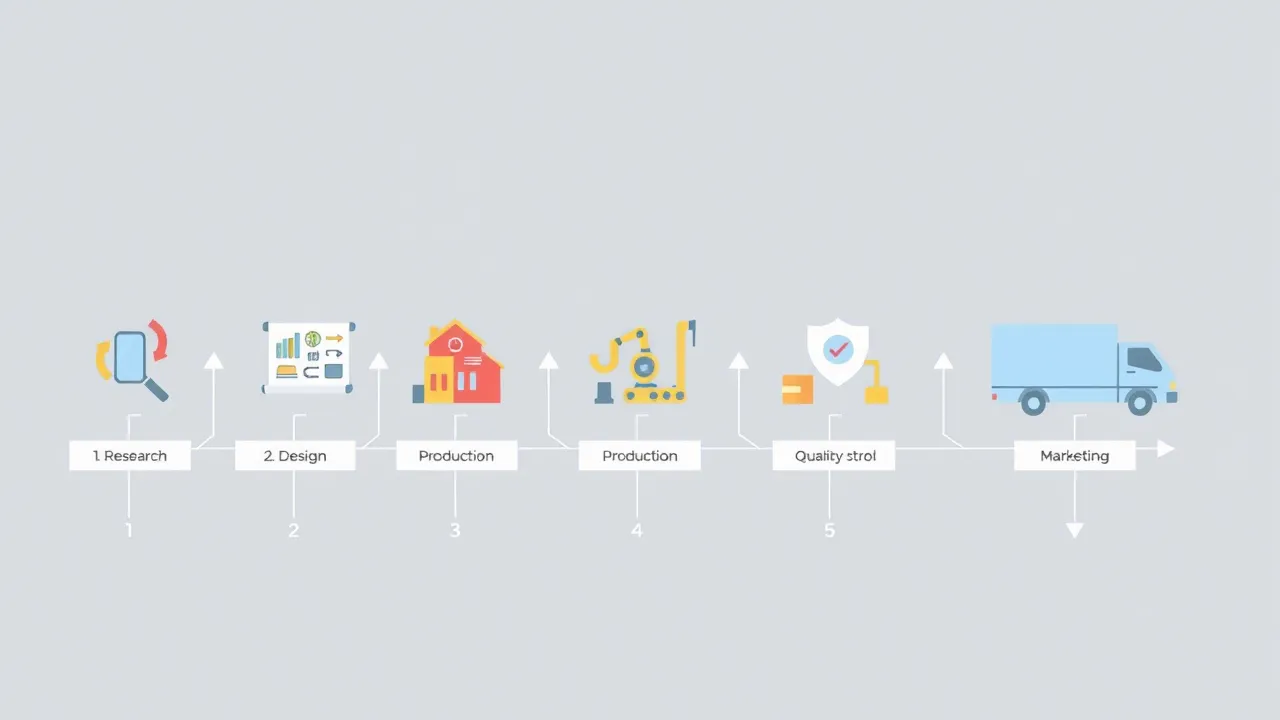
The industrial process refers to the transformation of materials into finished products through a series of stages. These stages can be divided into four main phases: research, design, production, and quality control. These phases are necessary to ensure a quality product and are used in the manufacturing of a wide variety of products.
1. Research
In the first stage, research, engineers study the product they want to create. This involves gathering information about materials, manufacturing processes, costs, delivery times, and safety requirements. A market analysis is also conducted to determine if the product will be successful.
It is a crucial step in the development of a new product as it involves collecting and analyzing information to identify the needs and desires of the market and the end user, as well as designing a product that meets these needs and desires effectively and efficiently.
The research stage usually includes different activities, such as:
-
Market research: consists of gathering information about the market in which the new product is to be launched, including size, competition, prices, and market trends. This information can be collected through consumer surveys, sales data analysis, and other methods.
-
User research: consists of gathering information about the needs and desires of the end user of the product, including their preferences, habits, and expectations. This information can be collected through interviews and consumer surveys, focus groups, and other methods.
Once the necessary information is collected, the second stage is
2. Design
Engineers use the information collected to design a product. This includes creating a detailed blueprint of the product and determining what materials will be used for its manufacture. The goal is to develop a final design for the product or service to be produced, which meets the needs and desires of the market and the end user and is viable from a technical and economic point of view. The design stage usually includes the following steps:
-
Design different product concepts that meet the needs and desires of the market and the end user. These concepts can be developed through brainstorming techniques and creative problem solving.
-
Test the designed concepts to evaluate their technical feasibility, their appeal to the end user, and their ability to meet the needs and desires of the market. These tests may include laboratory tests, prototype tests, and consumer tests.
-
Select the most viable product concept and develop a final design that includes all the technical and design details necessary to produce and market it.
-
Conduct performance and durability tests of the final design to ensure it meets quality standards and is viable from a technical and economic point of view.
-
Make adjustments to the final design if necessary to improve its quality and viability.
The third stage is
3. Production
Here, materials are transformed into finished products through a series of manufacturing stages. This involves creating prototypes, optimizing manufacturing processes, and assembling the product.
The production stage consists of carrying out the manufacturing process of the product or the provision of the service, using the necessary resources (such as machinery, materials, labor) and following a standardized and optimized production process. The production stage usually includes the following steps:
-
Plan production: consists of determining the quantity of products or services to be produced, the sequence of production processes, the necessary resources (such as machinery, materials, labor), and the timeframe in which they are to be produced.
-
Organize production: consists of preparing the production environment, including the arrangement of machinery, storage of materials, and distribution of labor.
-
Carry out the production process: consists of carrying out the manufacturing process of the product or the provision of the service following the established sequence and procedures.
4. Quality Control
Last but not least is the quality control stage. This stage comprises a series of exhaustive tests to ensure that the product meets quality standards. This includes performance tests, resistance tests, and durability tests.
Quality control of a product consists of performing different tests and measurements to ensure that the product meets the established quality standards. These tests and measurements are carried out during and after the production process, with the aim of detecting and correcting any problem or failure that may affect the quality of the product.
Quality control can include different types of tests and measurements, depending on the characteristics of the product and the established quality standards. Some common tests and measurements in quality control are:
-
Laboratory tests: consist of performing chemical, physical, or biological tests on the product to evaluate its quality. These tests may include nutrient analysis, contaminant content, durability, and other aspects.
-
Performance tests: consist of evaluating the performance and reliability of the product in real-use situations. These tests may include duration tests, resistance tests, and other aspects.
-
Durability tests: consist of evaluating the resistance of the product to different factors of wear or degradation, such as time, intense use, exposure to external agents, etc.
-
Quality measurements: consist of measuring compliance with the quality standards established for the product. These measurements may include measurements of size, weight, shape, tolerances, etc.
Once these tests have been completed satisfactorily, the product is considered suitable for marketing.
5. Commercialization
Once the manufacturing process of the product or the provision of the service has been carried out and the necessary quality tests have been carried out, the product or service is delivered to the customer. This delivery can be done in different ways, depending on the characteristics of the product or service and the preferences of the customer. Some common options for the delivery of products or services are:
-
In-store delivery: the customer can go to the store where the product or service is sold and pick it up there.
-
Home delivery: the product or service is sent to the customer’s home through a courier or transport service.
-
Digital download: in the case of digital products or services, the customer can download them directly from the internet.
Once the product or service has been delivered to the customer, the post-sale stage begins. The post-sale stage consists of providing support and additional services to the customer after the purchase of the product or service. These services may include warranties, returns, repairs, updates, and others. The post-sale stage aims to ensure customer satisfaction with the purchased product or service and to build loyalty for future purchases.
In conclusion, the industrial process is divided into four main stages: research, design, production, and quality control, plus a fifth which is the delivery to the customer or commercialization of the product. These stages are used to ensure that products meet quality standards and are safe for use. This allows companies to produce products of the highest quality at the lowest possible cost.